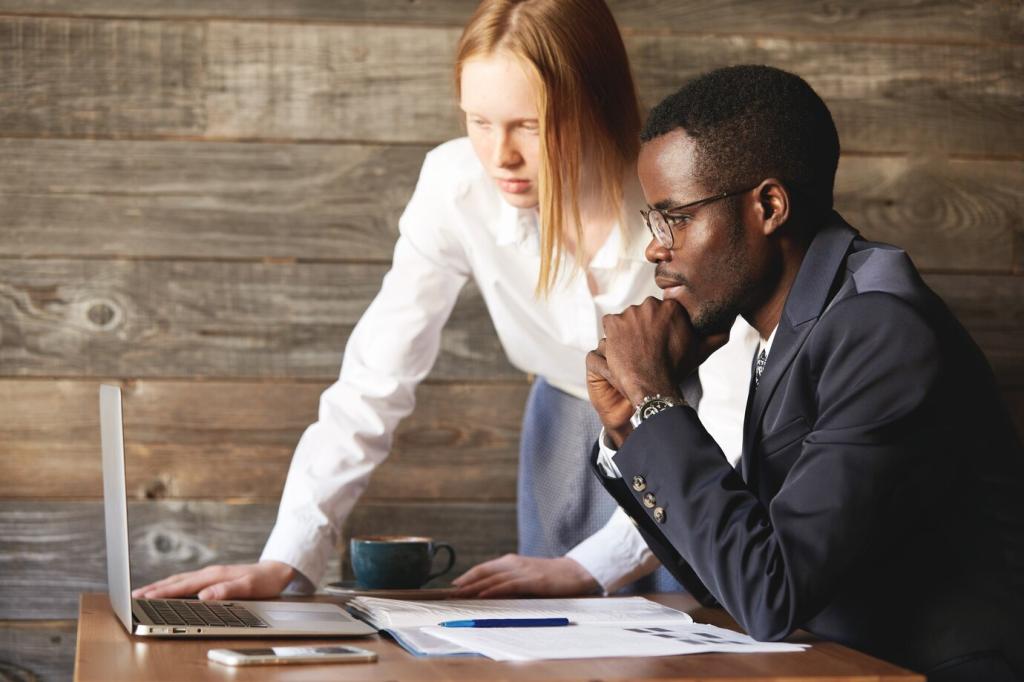
Invoicing and Documentation That Pass CRA Scrutiny
Include your legal business name, billing date, unique invoice number, description of goods or services, subtotal, tax rate and amount, and your GST/HST registration number. Accurate place‑of‑supply details ensure the correct rate, minimizing client disputes and rework.
Invoicing and Documentation That Pass CRA Scrutiny
Capture receipts immediately using a mobile app, tag by tax code, and reconcile weekly. Attach documents to transactions inside your software so context is never lost. Tell us your favorite tool, and we’ll compare options in a future post.